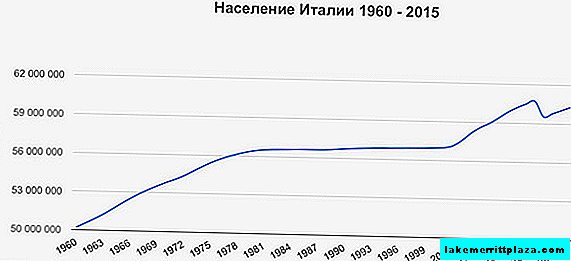
Over the past 55 years, Italy’s population has not increased by more than 0.99% per year. This country ranks fourth in Europe in terms of population, although for a long time it has been characterized by a crisis of reproduction and has a negative natural increase - since 1960, the number of Italians has increased by only 10 million. According to information for 2018, 59.9 million people live in the "Garden of Europe".
Ethnic evolution
Italians themselves like to call Italy not a "garden", but "Bel Paese" - a magnificent country. Such a flattering characterization is justified by cultural and historical premises. The Italian nation has a complex nature and the population of ancient Italy in this sense has undergone a difficult structural evolution. This formation is inseparable from the country's continued political fragmentation and the formation of the Italian language. The consequences of this natural development are in sight today.
Evolutionarily, the Italian population goes back to all sorts of ethnic entities. According to the administrative regions within the country, there are 21 indigenous sub-ethnic types:
- Calabrians
- Ligurians
- basilicants;
- Tuscans
- Sardinians;
- Sicilians and many others other
It is important to consider the existence of smaller structures - ethnic diasporas. The area of ethnic communities is indicated by the borders of the ancient provinces of the country. It’s impossible to say exactly how many people are in a particular group.

The lack of expression of national identity - Another interesting characteristic of Italians. Any of them is first Sardinian or Tuscan, and then Italian. These people are well aware of their pedigree and rarely miss the opportunity to emphasize their root origin.
In addition to sub-ethnic fragmentation, Italians themselves persistently emphasize the division of the demos into northerners and southerners. The dominant and prosperous north historically bore the status of a cultural and industrial region, while in the south agrarian life was in full swing. The urban population has always been a little isolated from the rural. Therefore, a regionally dependent northern and southern type of employment and income was formed.
South-North imbalance
Italy closes the top three economic giants of the Eurozone. Although the total number of financially active citizens in Italy exceeds 26.5 million people, the employment structure has a negative characteristic - a pronounced regional imbalance in earnings and a decrease in per capita GDP.
The percentage of employment was as follows:
- agriculture - 5%;
- industrial industry - 32%;
- tertiary sector - 63%.
GDP per capita in 2017 amounted to $ 38,140.
The gap between the industrial power of the north and the lush fertility of the south is manifested by the failure of the south (in contrast to the central region) to draw close to the industrial indicators of the north. While 3-4% of the inhabitants of northern cities in the agricultural sector are involved, in the south 12-14% of Italians work for agriculture.
Due to the zero per capita GDP growth rate in 2018, Italy has fallen into recession for the fifth time in the last 10 years. An incredible increase in unemployment overcame a 40-year record in the country. The urban population has reduced purchasing activity by almost 2%.
When calculating the per capita GDP, official statistics now provide for the amount of proceeds from the illegal activity of Italians (including drug trafficking, prostitution, tobacco smuggling). In 2014, such an accounting raised the national annual GDP by 2%, but even this did not save the Italian economy from stagnation. GDP in the state has been at a critical level since the spring of 2011. In 2015, this indicator is projected to decrease by another 0.3-0.5%. But if the economic problem can be considered temporary, then the demographic one is stable for Italy.
As of 2018, the natural growth in the state was set at a negative mark. The number of deaths is 10% per thousand people, while the birth rate is only 9%. This type of depopulation is called "winter" reproduction. But how does a negative characteristic allow Italy to hold onto 4th place in Europe? The general demographic picture is interesting here: composition and resettlement.
Beautiful country of immigrants and the elderly
According to the State Institute of Statistics, a positive effect on the population is provided by foreigners who have chosen the area of the northern and central region for permanent residence. From the point of view of migration growth, the last two years have been demographically successful for the country: while the indigenous population is struggling with the reproduction crisis, newcomers are changing the situation. The positive trend is explained by the active settlement of the Apennine Peninsula by immigrants from other European countries, Arabs, Asians. The average density in the country is 200 people per km2. This amount provides Italy 5th place in Europe.
Briefly, the characteristic of ethnic structure can be expressed as follows:
- Italians proper - 92.8%;
- Romanians - 2.4%;
- Asians - 1.2%;
- Albanians - 1%;
- Ukrainians - 0.6%;
- Americans - 0.5%;
- the rest is less than 0.5%.
In recent years, immigrants from the Maghreb and Asia began to actively overtake the number of immigrants from eastern Europe and North Africa, giving Italy a new ethnic composition. There are especially many gypsies and Chinese. In 2012, the total number of legal and illegal immigrants exceeded 4.2 million inhabitants, which is more than 7% of the main figure. Almost six hundred thousand children born in immigrant families make a considerable contribution to the country's demographic fund.
Features of the placement and residence of immigrants
- From 2000 to the present, the number of foreigners has tripled. The settlement area is almost 152,000 km2;
- 39% of visiting residents settled in the northern and northwestern region of the country. Internal migration from the south is directed to northern cities, because this area is most developed economically, the number of non-indigenous inhabitants here is 3.5 million people. Another 34% of citizens sheltered in the central region of the country, and only 13% of foreigners went to agriculture and stayed in the agricultural southern region;
- Due to the accumulation of non-indigenous inhabitants, the population density in Northern Italy reaches over 300 people per km2. Due to the high concentration of people in the northern cities, the average density in the country is also impressive: in Naples, over 2,000 people per 1 kilo square! Compare: in the mountains it barely reaches 40;
- about half of the visitors live in small ethnic communities, the percentage of Italian residents has a small proportion in them. An example of such accommodation can be considered the settlement of Brescia in Lombardy.
The intense influx of immigrants even justifies the shortage of natural reproduction, but also provokes an economic imbalance: the volume of GDP does not keep pace with population growth. Moreover, 67% of these people are not young people: in the last decade, the average age of the Italian city dweller has greatly increased, today it reaches 45 years. The nation is multiplying slowly and aging rapidly.
- We recommend reading: secrets of the centenarians of Sardinia
Population policy
Italy, like most developed countries, is inherent first type of reproduction (synonym for "scarce type") take a number of active measures to overcome depopulation and stimulate fertility.
Economic encouragement of parents
6% of the social budget is earmarked for family support. This amount is 30% lower than the EU average, but in the context of the fact that 64% of the social fund budget is spent on pension payments growing with the number of old people in the country and life expectancy, then 6% can be considered a decent indicator;
Payments to single parents, newlyweds and large parents
This type of family is correlated with a low level of income: the social assistance of regional authorities is expressed in free or reduced-price meals for children in schools and kindergartens, and lowering the price of travel by public transport. Payments for the repayment of rental housing and utilities. The size of benefits is tied to family annual earnings. With an annual income of parents up to 12 thousand €, the payment will be about 300 € per month, families with an income of more than 27.5 thousand € can count on 40 €, and help is not provided to spouses with a joint annual budget of 44 thousand €;
Development of schools and preschool institutions
The emergence of new municipal kindergartens, which are not enough in Italy, reduces family expenses on raising a child. In the meantime, the private type of schools and kindergartens prevails (60% for 2018);
By the way, if you believe the population counter, while this material was being written, 19 babies were born in Italy.








